SOC141 - Phishing URL Detected Alert
Let's analyze a phishing mail, with a suspicious URL ... (Event ID - 88)
It’s the first week of February and that just means one thing. Let’s Defend has released a new set of SOC Alerts for us blue teamers to investigate and solve and here, we will be solving the SOC 141— Phishing URL alert.
Let’s jump right into it!
NOTE: Always remember to investigate alerts from Let's Defend, on a VM.
Introduction to the Alert
These are the alert details being given to us:-

Let’s take ownership of the case
Reading the alert’s summary, it’s plain to see that a phishing URL was sent to the victim, wanting him/her to click it
Create a case book for the same

Collection of Data

Q) Please check alert details for the following below:-
Source Address Destination Address User-Agent
From the alert summary, we can determine
A) Source Address — 172.16.17.88 Destination Address — 192.64.119.190 User Agent — Mozilla — Windows
Search Log
Q) Please search in Log Management for details.
Let’s search the Source IP address, on the Log Management screen
We can see two corresponding entries for the address

Upon expanding the logs, we find the following information:-


Analyze URL Address
Q) Analyze URL in 3rd party tools. Please click “Malicious” if it is malicious and click “Non-malicious” if it isn’t.
You can use the free products/services below.
AnyRun VirusTotal URLHouse URLScan HybridAnalysis
Let’s analyze using our go-to go tools VirusTotal and Hybrid-Analysis
Taking the URL — http://nuangaybantiep.xyz, and searching it up on VirusTotal brought the following results:-

It says that the domain is not malicious at all Reading the comment under the ‘Community’ section gives us the following note:-

That’s why I stick by the rule of verifying with multiple platforms Reading Joe Sandbox’s HTML report of the malicious domain, we come across the following analysis of the domain:-

Seems like a malicious domain and is capable of spreading Trojan(take a look at the pie chart)
Let’s analyze it on the Hybrid-Analysis platform as well, where 2 search results pop up for the domain

Both incidents determine that the file is not malicious through
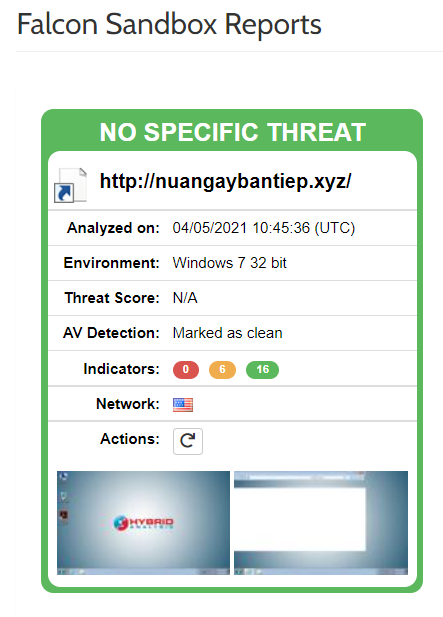
Though the domain may be distributing malware, it’s not classified as a malicious domain by these threat intel platforms.
Let’s click on “Malicious” and proceed forward
A) Maliciious
Has anyone accessed IP /URL Domain?
In the very next screen, we are asked to provide answers to the following questions:-

From the log expansion evidence provided above, we can answer these:-
A) Apr, 04, 2021, 11:10 PM
A) 172.16.17.88
A) 192.64.119.190
A) Mark
A) Mozilla — Windows
A) No
A) Yes
Containment

Proceed to contain the victim host
Submission of case artifacts
In the very next screen, we are asked to submit artifacts derived from the case
From the ‘Links’ tab of the domain’s analysis on VirusTotal, we can see some outgoing links from it

Unable to graph any mail addresses from this suspicious domain, we can very well state that the origin of the attack is from Reykjavik, the capital of Iceland
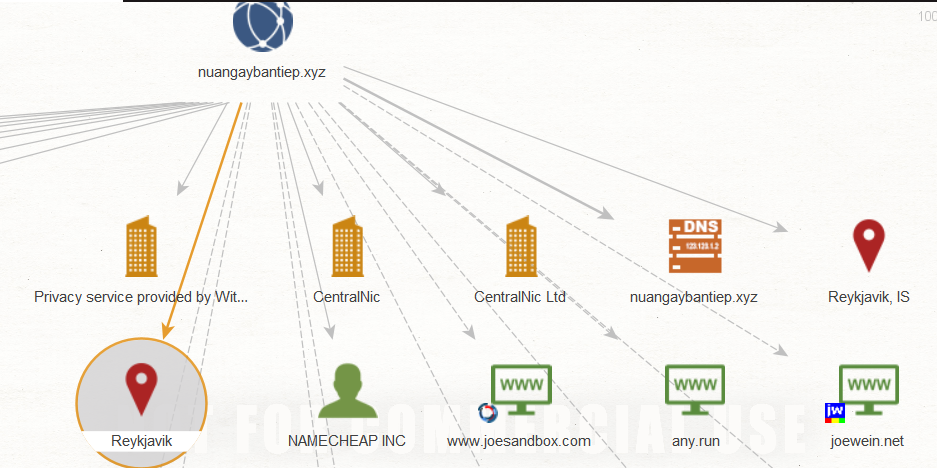
Mapped using Maltego
This is what the malicious domain looks like
Case Artifacts

Analyst’s Note
Finish the playbook!
Close Alert
Proceed to close the alert and provide parting remarks about the case

Alert Scorecard
This is awesome!

Every alert solved is a step towards perfection and I am pretty happy with the score I received.
Summary of the alert
A phishing mail was sent from source 172.16.17.88, with a suspicious link embedded within it. Unfortunately, the victim ended up falling for it. Relevant network logs provide evidence of this. The suspicious domain was analyzed and showed evidence of peddling malware in the past
The case was a true positive for a phishing attack and the analyst responsibly provided artifacts and notes, discussing the case characteristics and results
Conclusion
This SOC alert exercise was a breath of fresh air, as I performed threat hunting after repeated blue team activities on Try Hack Me.
Thank you for reading this blog entry. Stay tuned, as I go hunting behind some pcap files out there....
Your opinion matters
My audience has a voice. Feel free to reach out to me, on my socials (links are on top of this page) for any queries to be addressed. Dropping a sweet message would make my day
Let your opinion about this write-up be known, by selecting any one of the emojis below!
Last updated